There is an adage that is often still heard in the fire service, “100 years of tradition unimpeded by progress”. When it come to be effective firefighters this old saying no longer applies. These Cutting-Edge Tools for Firefighters are state of the art in the fire service.
Firefighter love and cherish their traditions and proud history. Throughout my years as a firefighter and Fire Chief I saw this on a nearly daily basis. At times this was taken so far that safety was, in my opinion, compromised because of these strong beliefs. Yes, I can already see the hate emails building up in my inbox.
Change can be tough, especially in the fire service. As quoted by Retired Phoenix Fire Chief Alan Brunacini stated: “Firefighter hate two things; change and the way things are”. With this being said, I think in some areas we are seeing change that will improve safety and efficiency.
To pursue a career as a firefighter, it is essential to meet specific education and training requirements. While a high school diploma or equivalent is the typical entry-level education, additional post secondary instruction and certifications are often necessary for aspiring firefightersIn this world of ever-changing advancements in communication, and technology Firefighter are now welcoming changes in the fire service this are so proud of.
Firefighters now have access to cutting-edge tools that revolutionize their ability to combat fires, navigate hazardous environments, and save lives.
In this blog post, we will explore the latest advancements in firefighting equipment, discussing how these tools have evolved and how they contribute to the safety and success of firefighters on the front lines.
We will also examine the tools and technology available for incident command, empowering leaders to manage complex operations efficiently.
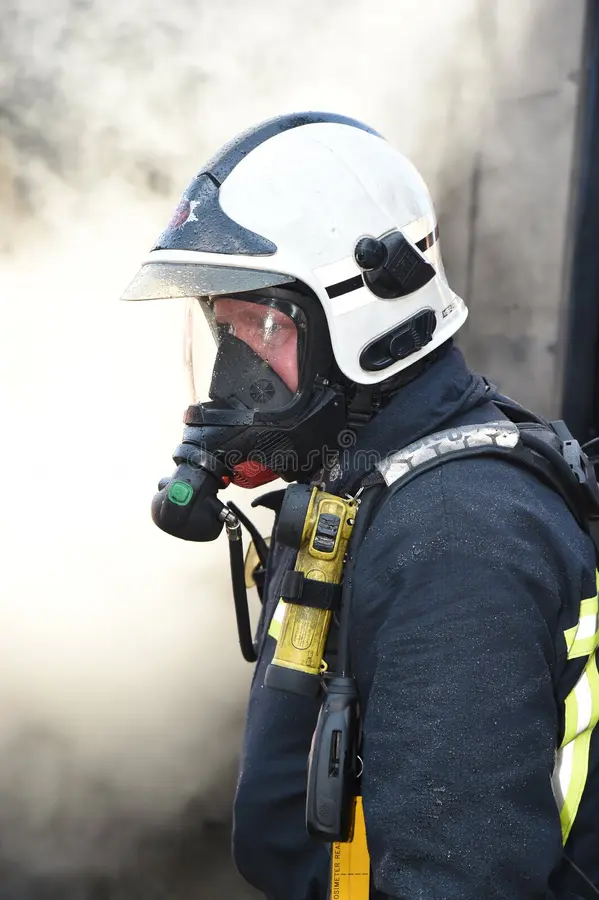

Evolution of Firefighter Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is the first line of defense for firefighters. This PPE, often called Turn-out gear or Bunker Gear, has undergone significant improvements to provide enhanced protection and comfort.
Modern firefighting PPE are now made of advanced fire-resistant materials, such as aramid fibers and advanced synthetic blends, that offer increased thermal protection while remaining lightweight and flexible. This new bunker gear incorporates moisture-wicking technologies, such as breathable membranes and moisture-resistant liners, to keep firefighters cool and dry during intense firefighting operations. Some PPE also includes built-in cooling systems that circulate cool air to prevent heat stress.
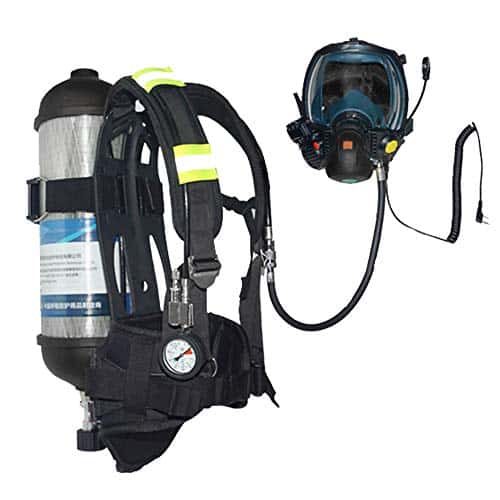

Advancements in Firefighter Breathing Apparatus:
Breathing apparatus is a critical component of a firefighter’s gear. It enables Firefighters to navigate smoke-filled environments safely. Often referred to as SCBA, Self Contained Breathing Apparatus, these self contained breathing systems have seen advancements with improved features that have improved safety will extending work time in hazardous environments.
Newer SCBAs offer enhanced filtration capabilities, providing cleaner air to firefighters and protecting them from toxic gases, particulate matter, and chemical contaminants.
New SCBAs are also often equipped with advanced monitoring systems that track vital signs, air supply levels, and alarm functions, ensuring the well-being of firefighters during operations.
Additionally, some SCBAs incorporate heads-up displays (HUD) that provide real-time information about air supply, thermal conditions, and communication data, allowing firefighters to maintain situational awareness without compromising visibility.
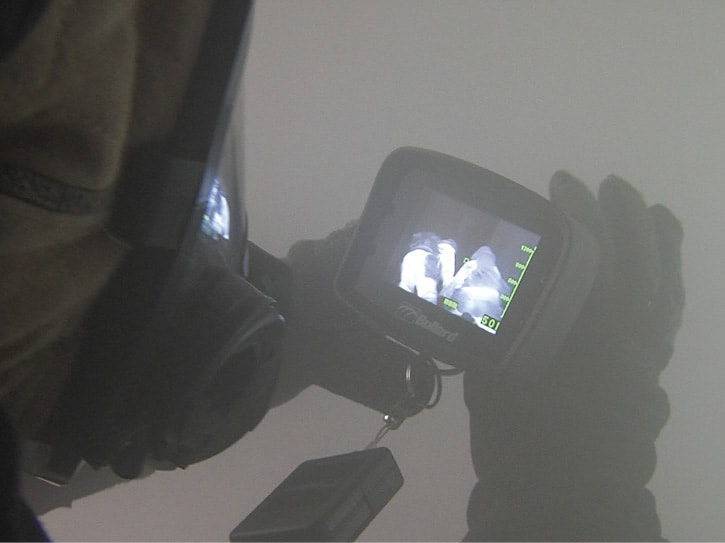

Firefighter Thermal Imaging Technology:
Thermal imaging cameras have been a welcome tool for firefighters for some time now. There “cameras” allow firefighters to “see” through smoke and darkness. However, new advances have made these tools more effective, lighter, and smaller. In some cases, even incorporating them in SCBAs.
The latest thermal imaging technology provides sharper and more detailed images, enabling firefighters to quickly identify hotspots, locate victims, and assess structural integrity. These cameras now offer higher resolution and sensitivity, allowing for greater clarity in identifying potential hazards.
Additionally, advancements in image processing algorithms and software have improved image analysis capabilities, enabling firefighters to detect hidden fire sources and track changes in temperature patterns more effectively.
Thermal imaging cameras are now more compact and lightweight, making them easier to carry and use during firefighting operations.

Revolutionary Fire Suppression Tools:
Advancements in fire suppression tools have led to more efficient and effective firefighting techniques. One notable innovation is the development of compressed air foam systems (CAFS).
CAFS combines water, foam concentrate, and compressed air to create a high-expansion foam Blanket. This foam blanket covers the fire rapidly reducing heat and suppressing flames.
This technology significantly improves firefighting operations by maximizing water usage, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing firefighter safety.
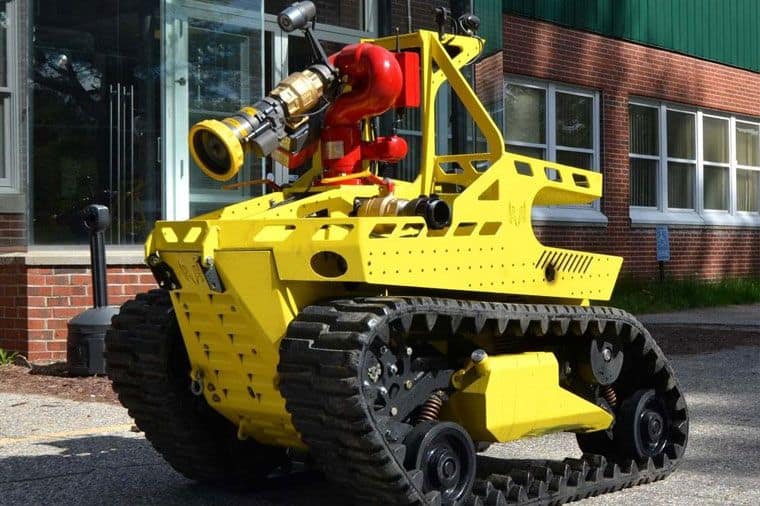
Other new fire suppression systems starting to make their way into the fire service include robotic platforms that can be remotely operated, allowing firefighters to maintain a safe distance while combating fires in hazardous environments.
These robots are equipped with high-pressure water cannons, specialized nozzles, and thermal cameras. This enables firefighter to extinguish fires in challenging locations while minimizing firefighter exposure to danger.
Improved Communication and Tracking Systems:
Communication and tracking systems have become essential in promoting efficient coordination and ensuring firefighter safety. Advanced radio systems with enhanced range, clarity, and multiple channels enable seamless communication.
Read more about new incident command technology by click here
These systems also support encrypted communication, ensuring secure and confidential information exchange during critical operations.
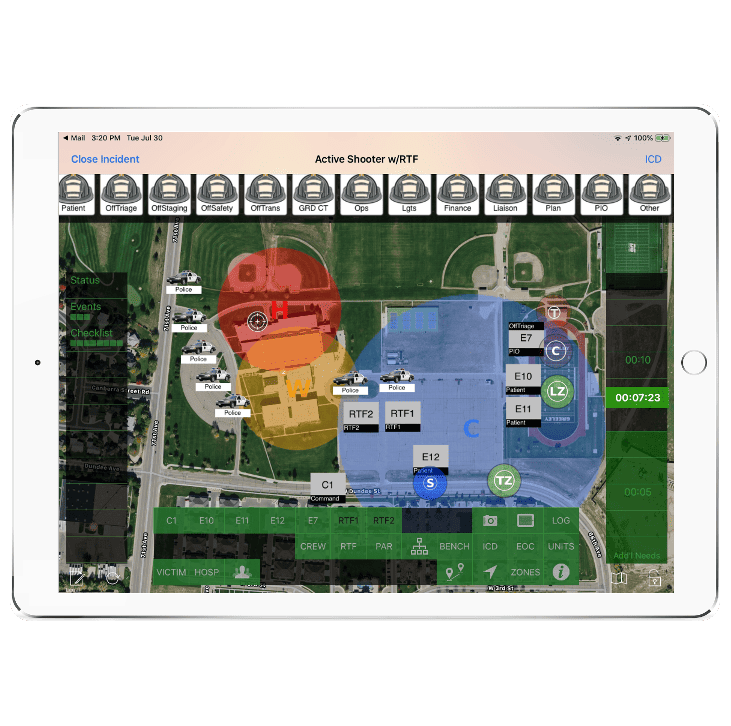
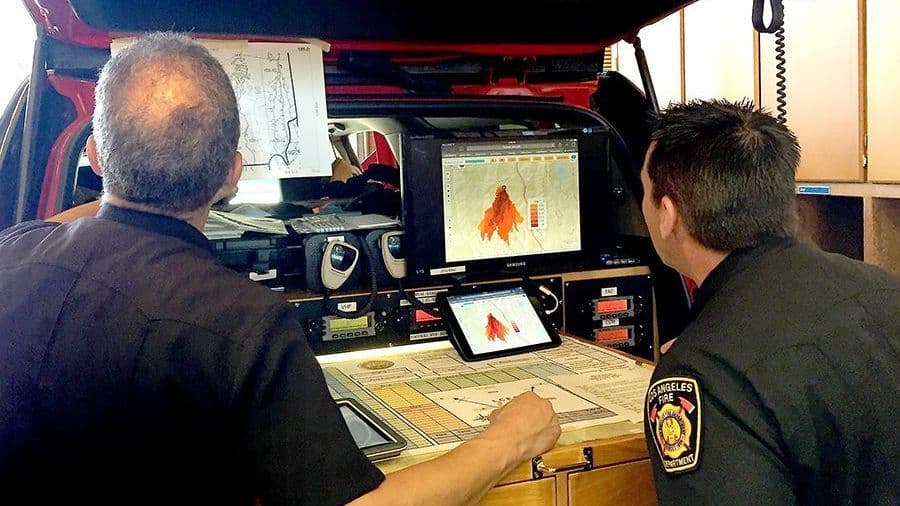
Incident commanders can utilize incident management software platforms that provide real-time incident tracking and resource allocation. These software solutions enable commanders to have a comprehensive overview of the incident, including the location of firefighters.
Some software platforms also integrate with mobile applications, allowing firefighters to access critical information on their smartphones or tablets.

Tools and Technology for Incident Command:
In addition to equipment for individual firefighters, incident commanders require specialized tools and technology to effectively manage complex firefighting operations.
Incident command systems (ICS) have evolved to become more sophisticated, offering comprehensive solutions for coordination and decision-making. These systems provide incident commanders with a structured framework to manage resources, establish and facilitate effective communication among response teams.
Incident command software platforms offer a centralized hub for incident management, allowing commanders to monitor resources, track incident progress, and allocate tasks efficiently.
These platforms may include features such as real-time incident mapping, resource tracking, status boards, and communication logs.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a vital role in incident command. These systems integrate mapping providing detailed information about the incident area. These details can include building layouts, hydrant locations, and potential hazards.
GIS enables incident commanders to create accurate incident action plans, make informed strategic decisions, and communicate critical information to response teams effectively.
Incident commanders can benefit from mobile command centers that serve as a central hub for managing operations on-site. These command centers are equipped with advanced communication systems, data analysis tools, and video monitoring capabilities.
These mobile command tools facilitate coordination and information sharing among various teams and agencies involved in the response effort.
Emerging technologies like drones have also found applications in incident command. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors, drones can provide real-time aerial views of the incident scene.
This will assist commanders in assessing the situation, identifying hotspots, and determining the effectiveness of firefighting operations.
Drones can also be used to deliver essential supplies to firefighters in remote or hazardous areas, conduct reconnaissance missions, and support search and rescue operations.
The constant evolution of firefighting equipment and tools has significantly enhanced the safety and effectiveness of firefighters.
From improved personal protective gear to cutting-edge thermal imaging technology to sophisticated incident command systems, these advancements empower firefighters to face the ever-changing challenges of their profession.
As technology continues to advance, it is crucial for firefighters to stay updated with the latest tools and equipment. This will ensure that those on the front lines have the best resources available to protect lives, property, and themselves.
The future of firefighting looks promising, with ongoing innovations driving the industry forward and enabling firefighters to perform their duties with even greater efficiency and safety.